
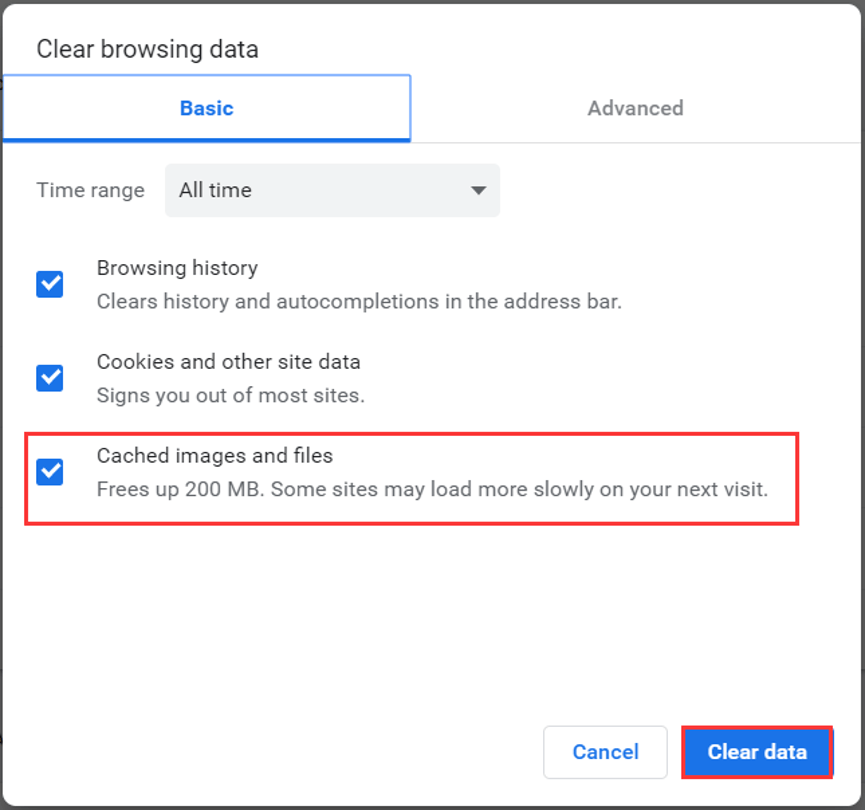
Access the Run command through the Start menu or using the shortcut Windows key + R. You can also find Chrome’s cache folder using the Run command. For example, for Google Chrome it looks like this: C:\Users\USERNAME\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\Cache. Following a flush, the request is answered again by the responsible DNS server, and the connection setup to the web project works as planned again. On Windows, the path to locate the browser cache is a little different. Solve technical problems: A DNS flush can resolve technical problems when accessing web applications, e.g., if an incorrect version of the called website is displayed due to outdated entries.So-called DNS spoofin (or DNS cache poisoning) is intended to tap sensitive login data, for example, user details for online banking. Choose the types of browsing data you want to clear (see the table below for descriptions). Under Time range, choose a time range from the drop-down menu. Under Clear browsing data > Clear browsing data now, select Choose what to clear. Check the boxes for the temporary cache files you want deleted, then click 'Remove Files. Select Settings and more > Settings > Privacy, search, and services. Security against manipulation: If cybercriminals gain access to the DNS cache, they could manipulate entries and redirect you to fake websites. Open the Windows 11 settings menu and go to System > Storage > Temporary Files.The more extensive the collection of cached addresses, the more you reveal about yourself. Hide search behavior: Recorded addresses including additional information such as validity period provide an approximate overview of your page history.There are three reasons for regularly setting the DNS register to zero with a DNS flush, regardless of the actual validity period of the individual records:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
